Soil survey types
Over 150 soils and land resource mapping projects have been carried out in Queensland since the mid 1950s.The following is a summary of the major soil survey types.
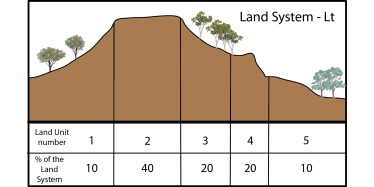
Land systems surveys
Land systems are recurring patterns of geology, topography, soil and vegetation.
They are usually mapped at a broad scale (greater than 1:250,000).
Most of the land systems mapping in Queensland was conducted in the 1950s and 60s.
A typical land system is split into several land units. These land units may not be mapped but only described in reports. Land units are distinctive landscape positions (within a land system) with characteristic soil–vegetation associations.
A land system map will typically describe:
- a general overview of the entire land system (geology, landform, soils and vegetation)
- a more detailed overview of the individual land units.
Example
The following is an example of the type of information presented in a land system survey.
| Land system (Lt)Broader description of the entire land system | Land unit 5More detailed overview (land units are usually not mapped, only described) |
|---|---|---|
| Geology | Lateritised tertiary basalt and exposed unweathered basalt | Recent alluvia |
| Landform | Steep hills and scarps. Frequent rock outcrops and stony areas. | Plain and levee-slopes 3% |
| Soils | Very shallow, dark reddish-brown clay loams grading into dull reddish brown or light clays on scarps and shallow dark cracking clay soils on lower slopes | Brownish black fine sandy loam to clay loams grading to brown and dark reddish-brown clays, deep to very deep soils |
| Vegetation | Spotted gum, narrow-leaved ironbark/red ash forest on scarps and silver-leaved ironbark, gum-topped bloodwood kurrajong grassy open forest on clays | Silver-leaved ironbark open forest with scattered gum-topped box open forest |
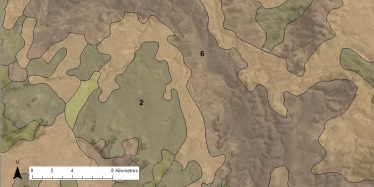

Land resource area surveys
Land resource areas are units of land based on geological and landform characteristics with a recurring pattern of soils and vegetation.
Land resource area surveys are usually conducted to give a broad overview of the region.
Each land resource area contains a range of common and associated soils that are usually outlined in detail in the published reports.
Example
The following is an example of the type of information presented in a land resource area survey.
| Land resource area 6—ranges | Land resource area 2—undulating scrub plains | |
|---|---|---|
| Landform | Undulating to very steep hill mountains and occasional mesa formed on sedimentary rocks, metamorphics and minor volcanics | Undulating plains and rises developed on sedimentary rocks, tertiary basalt and unconsolidated sediments |
| Soils | Stony lithosols, shallow sand and loams, minor red and yellow earths, red-brown earths, non-calcic brown soils and solodic soils | Mainly solodic soils with minor red-brown earths non-calcic brown soils and sands |
| Vegetation | Woodlands of narrow-leaved ironbark, silver-leaved ironbark, ghost gum | Woodlands of poplar box, silver leaved ironbark and narrow leaved ironbark |
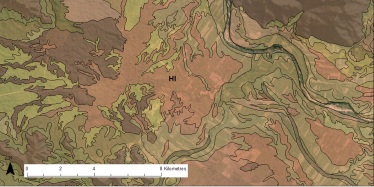

Soil surveys
Soil surveys are maps of particular soil types based on soils having similar properties. Soils are usually defined as one of the following:
- soil profile class—defined as a group of similar soils, having soil profile properties in common
- soil phases—a subdivision of a soil profile class based on attributes that have particular significance for land use, such as shallow phase, where the soil depth is predominantly shallow and may influence particular land uses
- soil variants—a soil with one or more attributes outside the usual range for a defined soil profile class, but because of its restricted distribution (or because the varying properties are not considered to have particular management significance), it is not defined as a separate soil profile class
- soil associations—compound mapping units which generally contain 60% or more of one soil profile class.
Example
The following is an example of the type of information presented in a soil survey.
Soil profile class—Hamleigh (Hl) | Description |
|---|---|
| Concept | Bleached, strong mottled, grey or yellow-brown duplex soil with a thin (0.25m) A horizon and a sandy D horizon developed on the alluvial plain |
| Australian soil classification (ASC) | Vertosol |
| Principal profile form (PPF) | Ug3.2, Ug5.24, Ug5.16. Uf6.41, Ug5.5 |
| Great soil group | (Bleach) grey clay |
| Morphology | Full description of the generalised soil profile for this class |
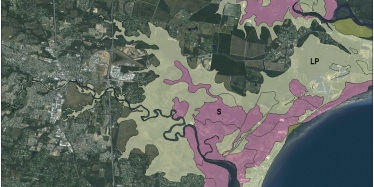

Acid sulfate soil surveys
Acid sulfate soils mapping is a specialised type of soil survey focusing on the identification of acid sulfate soils.
For more information, go to the online library catalogue and search for our fact sheet on interpreting acid sulfate soils maps.
Example
The following is an example of the type of information presented in an acid sulfate soil survey.
| Mapping unit | Description |
|---|---|
S | Acid sulfate soils on relatively undisturbed land: Land where acid sulfate soils occurs within 5m of the surface. Virtually all land in this category has at least 1 ’potential acid sulfate soil’ layer and some of this land will have an ‘actual acid sulfate soil’ layer. |
| LP | Land with low probability of acid sulfate soil occurrence: Land between the 5m AHD contour and the outer limit of Holocene, estuarine acid sulfate soil (i.e. the land <5m AHD) as mapped at this scale, with low probability of acid sulfate soil occurrence. Limited field investigation. |
More information
View soils data to access reports, maps or spatial data on the many soil and land resource surveys available across Queensland.


